Research Labs / Facilities
MRPC is a unique laboratory with preservation and digitization facility and complete recovery of physical documents. MRPC was launched in Irinjalakuda, Central Kerala as a part of University Grants Commission (UGC) endorsed course of Bachelor of Vocation Studies (B.Voc) scheme. MRPC handles kinds of Palm leaf documents and all forms of paper documents. Complete technical facilities are available for the preservation and digitization techniques. This includes Ink fixing, aqueous cleaning, solvent cleaning, bleaching, de-acidification, encapsulation, repair and lamination and full range of Digital Preservation.
Reach Out
When in 2018 and 2019 Kerala witnessed the worst floods that displaced nearly a million people, the MRPC team professionally assisted the public to restore thousands of important documents relevant to their personal lives. Nearly 50,000 documents which were torn, muddled inseparably with sludge and silt were recovered in this restoration effort.
Preserving History
Preservation of traditional palm-leaves is an on-going task that moves along with the B.Voc Course. The centre makes accessible the treasure of such documents to re searchers and scholars world-wide, on request.
Consulting
The center has helped institutions and banks to preserve many of their valuable documents as a part of the consulting initiatives of the center. We have assisted local bodies schools and individuals too. Please contact us for testimonials and to know how we can help your organization to preserve your history.


Plant tissue culture laboratory of our institution strongly promotes interdisciplinary research by providing several plant tissues culturing techniques and handling different funded research projects. Projects include In vitro studies on adventitious and hairy root induction in Withania varieties for enhanced metabolite production, including suspension and bioreactor culture. There are projects that aim to conserve some endangered plant species and wild orchids. Collection includes 42 varieties of endangered plant species. Some rare varieties include karutha inji, krishnanaal, karimanjal, dordtinia, nagadhanthi, agasthyathulasi, kolamaram etc. A few wild orchids from Western Ghats are also being conserved under the project which include Acampe praemorsa, Rhynchostylis retusa, Pholidota imbricate, Cymbidium aloifolium, Bulbophyllum neilgherrens Wight etc. Phytochemical test of different plant varieties are also analyzed and recorded in our plant tissue culture laboratory. Besides all these tissue culturing approaches we currently focused on noval nanoparticle based fluroscent staining techniques on live plants and it’s found to be a successful approach, another funded project on molecular mechanism of anti-proliferative activity of unexplored plants belonging to Sapotaceaefamily using human normal and cancer cell lines” are the ongoing works

Animal tissue culture involves in vitro maintenance and propagation of isolated cells, tissues or organs in an appropriate artificial environment. Cell culture is a significant tool for biological research. It is a great way to study issues that study cell metabolism and helps to understand the cell biochemistry. It also permits observation of the effects of different chemicals like drugs and proteins on various cell types. In animal tissue culture the majority of cells are anchorage-dependent and therefore require a solid or semi-solid support in the form of a substrate (adherent or monolayer culture), whereas others can be cultured in the culture medium, called a suspension culture. Animal, plant and microbial cells are always cultured in predetermined culture medium under controlled laboratory conditions. Animal cells are more complex than micro-organisms. Due to their genetic complexity, it is difficult to determine the optimum nutrient requirements of animal cells cultured under in vitro conditions. They require additional nutrients compared to micro-organisms, and they usually grow only when attached to specially coated surfaces. Nutritional requirements include a substrate or medium that provides support and essential nutrients such as amino acids, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, growth factors, hormones and gases (O2, CO2). All these factors control physical and chemical factors such as pH, osmotic pressure and temperature (37°C). Cell culture technologies have emerged as a tool to assess the efficacy and toxicity of new drugs, vaccines and biopharmaceuticals, and also play a major role in assisted reproductive technology.

Innovation Centre for Natural Resources is an initiative of the Department of Botany to provide support and training for students in transforming their ideas to develop innovative products that are beneficial to the society and nature. The innovation Centre aims to is design novel products that will reduce environmental issues and train young minds to become job creators and not job seekers. This initiative of the department elicit critical thinking among students and develops an insight in the students to explore the available natural resources in their niche and convert them novel products which are the need of the current scenario
Activities at a glance
Phytorevita Herbal cosmetics
Conventional cosmetics contain a high percentage of petroleum-based ingredients, which are harmful to the skin. Natural or herbal cosmetics are not just beauty products, but a recreation of nature in perfect harmony with our bodies and our world. Natural cosmetics are complex mixtures, such as those from plant extracts and oils, help to protect, nourish and hydrate the skin providing natural protection and care to our skin. Natural and organic cosmetics help us keep our well-being in-check. Their representation of nature through natural fragrances and delicate textures makes us feel closer to it and awakens our senses. Indeed, many natural essential oils from plants such as lavender, rose or mint are used in aromatherapy as they help to activate, relax and soothe our bodies.
Phytorevita herbal cosmetics
- Hair mask
- Face mask
- Face glow
- Skin brightening oil
Phytorevita Herbal beauty parlor
Phytorevita Herbal beauty parlor provides an abode for youngsters to rejuvenate their skin with herbal cosmetics produced by our Centre. Our products reassure consumers about the authenticity, origin and quality of these products.
Water Hyacinth Treasure Hunt
In the past Water Hyacinth is considered as a nuisance weed, now it has turned in to a potential treasure for future generations. The clean India campaign and Green India ideology has taken steps to clean rivers by making them free from water hyacinth. Water hyacinth in still river has adverse effect on water transport. So as to prevent the water hyacinth build up in the river, R&D strategies were developed to convert water hyacinth into useful products. Water hyacinth gives in valuable products like biogas, bioethanol, biohydrogen, paper, grow bags, biofertilizers etc The Innovation center aims to train students to make paper and grow bags to replace plastic bags out of this water hyacinth. In collaboration with Christ College of Engineering Irinjalakuda, research is undergoing to study the prospects of using Water hyacinth as filling material in road construction. Our next initiative is to train local people to produce Biogas from Water Hyacinth. MoU has been signed with Sanathana Dharma College Alappuzha to transfer the know-how of converting Water hyacinth to Wealth

Engineered nanomaterials exhibit interesting interactions with light providing
novel and unique ways to control many aspects of electromagnetic radiation. Harnessing the linear and nonlinear optical properties of nanomaterials offers unprecedented opportunities to
create ultra-compact devices such as optical limiters, optical sensors, optical switches, and most importantly, all-optical analogs of diodes, transistors and logic gates. The Nanomaterials Lab at St. Joseph’s College, Irinjalakuda focuses on the synthesis and nonlinear optical studies of metal nanostructures and their hybrids. Metal nanoparticles hold great technological promise because of the possibility of engineering their electronic and optical properties through material design. Metal nanoparticles such as Au and Ag are synthesized using chemical reduction method and green chemistry. Their nonlinear optical properties are studied using pulsed lasers in the nanosecond and femtosecond timescales. Furthermore, in an attempt to enhance the nonlinear optical properties of metal nanostructures, novel hybrids are developed using materials such as liquid crystals, organic chalcones etc.

The communicable Disease Research Laboratory has been working since 22nd November, 2013. CDRL functions in areas where a more concreted public health response is required in order to decrease the present and future burden of communicable disease on society and health care systems. The laboratory activities are coordinated by a scientific officer, nine research scholars under the supervision of the Director. At present the laboratory has 2 funded ongoing major research project (DBT, Randox (UK). Two major projects had completed this year. Beyond the two ongoing Major Research Project, the laboratory could submit six research proposals worthy of 10 million rupees to various funding agencies. The laboratory has already established three mosquito colonies of culex quinquefasciatus, Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus successfully which are the vectors of many deadly communicable diseases in Kerala. In this year, we were able to build a separate colony room for mosquito rearing. We have also maintained a continuous culture of microbial consortia that have been inhabited in the mosquito vectors. As a result of the continuous effort of different dimensions, the laboratory in 2020-21 published 11 research articles in peer-reviewed international journals and achieved 753 international citations. The published papers cope with diversity vectorial capacity and breeding habitats of mosquitoes, and possible means of control it and also in the field of cancer studies. 3 Postgraduate students from Department of Biotechnology, St. Joseph’s College Irinjalakuda and 3 Postgraduate students from Department of Zoology and Botany, St. Joseph’s college Irinjalakuda had been completed their PG project and dissertation from this lab.

Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy relies on the fact that the most molecules absorb light in the infra-red region of the electromagnetic spectrum. This absorption corresponds specifically to the bonds present in the molecule. The frequency range are measured as wave numbers typically over the range 4000 – 600 cm-1. This simultaneously collects high-spectral-resolution data over a wide spectral range. This confers a significant advantage over a dispersive spectrometer, which measures intensity over a narrow range of wavelengths at a time. FTIR is an extremely useful technique for confirming the identity of pure compounds. The technique is based upon the identification of functional groups within molecules where such groups vibrate (either through stretching or bending in various ways) when irradiated with specific wavelengths of light. FTIR analysis is used to understand the molecular structure of materials as well as the kinetics, mechanism and pathways in chemical reactions and catalytic cycles. This technique is used to the analyse solid and liquid samples.

A gas chromatograph (GC) is an analytical instrument that measures the content of various components in a sample. The analysis performed by a gas chromatograph is called gas chromatography. The sample solution injected into the instrument enters a gas stream which transports the sample into a separation tube known as the column. The various components are separated inside the column. The detector measures the quantity of the components that exit the column. To measure a sample with an unknown concentration, a standard sample with a known concentration is injected into the instrument. The standard sample peak retention time (appearance time) and area are compared to the test sample to calculate the concentration. GC analysis is used to calculate the content of a chemical product, for example in assuring the quality of products in the chemical industry; or measuring toxic substances in soil, air or water. GC is very accurate if used properly and can measure picomoles of a substance in a 1 ml liquid sample, or parts-per-billion concentrations in gaseous samples.

An inverted microscope is used to observe living cells in their natural conditions without damaging their viability.

UV-visible spectroscopy is an analytical method that can measure the analyte quantity depending on the amount of light received by the analyte.
Specific applications include measuring the concentration of substances such as proteins, DNA, or RNA; quantitation for other biochemical reactions; bacteriological cell synthesis; and enzymatic reactions.

PCR is a technique used in molecular biology to generate hundreds to millions of copies of a specific DNA sequence by amplification of a single copy or a few copies of a segment of DNA through multiple orders of magnitude.

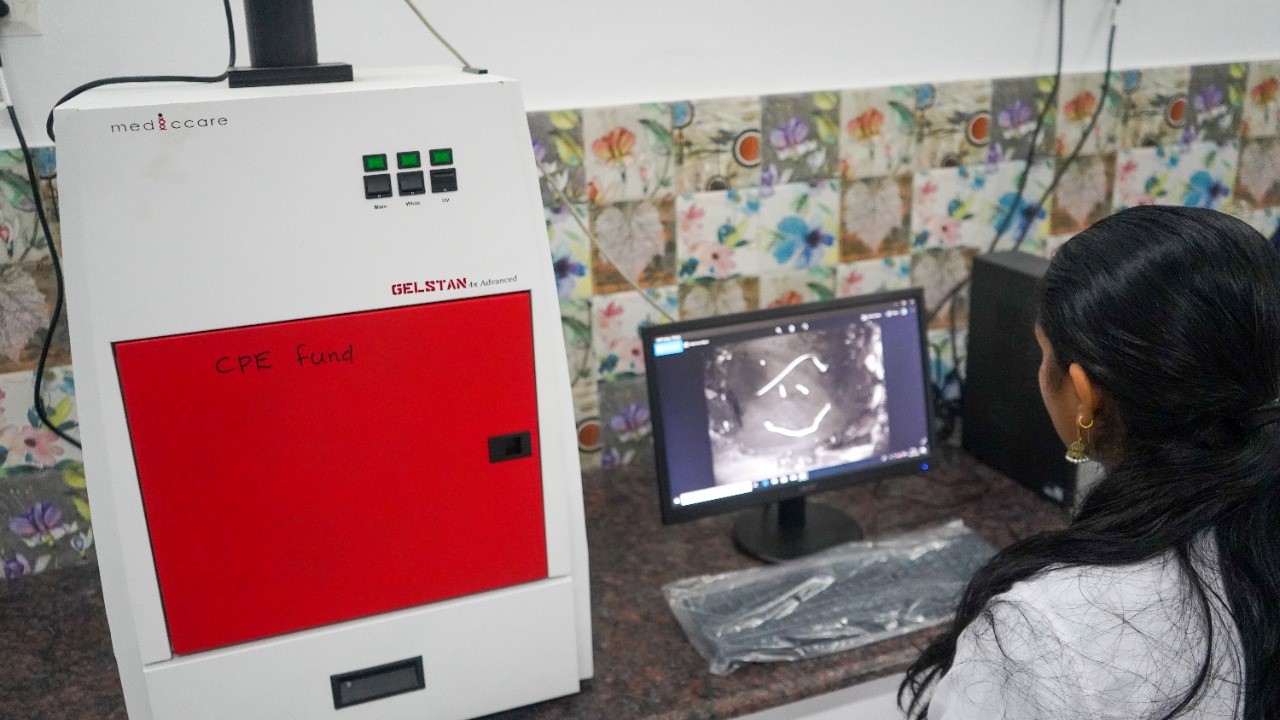
Gel documentation is used to record labeled nucleic acid proteins in various mediums such as agarose, acrylamide, and cellulose, which are commonly stained with ethedium bromide or fluorophores.
The BOD incubator is used to provide the ideal temperature and conditions for the microorganisms to grow and consume oxygen. The incubator typically has temperature control, which is set to 20°C, the standard temperature for BOD testing. The incubator also provides a dark and sealed environment to prevent any external light or air from entering the chamber. This is important to ensure that the only source of oxygen for the microorganisms is from the water sample.

A stereo microscope can be used for a wide range of applications because it has the ability to show structures in three dimensions. This microscope can be used for dissections, to study the morphology of inects without dissection, flowers, and other plant structures





